Why Transformer is constant flux machine?
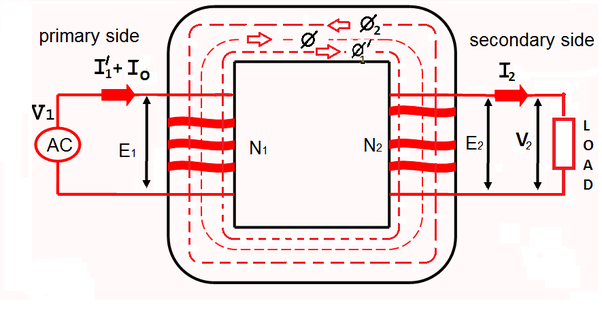
- When the supply voltage V1 is given to the transformer primary winding, primary current I1 flows through the winding which produces maximum flux Φm in the core.
- When the secondary winding of the transformer is loaded, the secondary current I2 flows through it.
- The secondary current I2 sets up its own mmf N2I2 and its own flux Φ2 which opposes the main or primary flux Fm.
- Therefore the resultant flux and primary induced emf is also decreased.
Resultant flux Φ = Φm – Φ2
- The supply system draws more current from the primary winding due to difference between supply voltage V1 and induced emf E1 increases until the original value of flux or main flux Φm is obtained.
- Let the additional primary current be I2‘. This current is equal in magnitude with I2 but anti phase with I2.
- The current I2‘ is known as reflected load current.
- The current I2‘ sets up flux Φ2‘ in magnitude. Therefore the mmf N1I2‘ and mmf N2I2 cancel each other.
- We can say that the magnitude and phase of load component of primary current depends upon the type of load.
- The net flux passing through the core remains constant whatever the load conditions if we neglect primary and secondary leakage fluxes
